822 Views
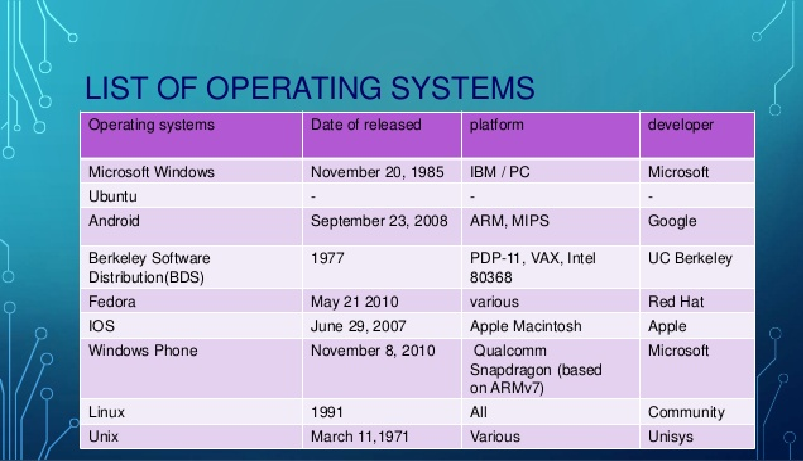
In computer science , an operating system is a set of programs that directs the use of the capabilities of a computer by application software .
Summary
1The main
- 2Other operating systems
- 3Experimental operating systems
- 4Smartphone operating systems
- 5TV operating system
- 5.1System developed by standardization bodies or industrial consortia
- 5.2System developed by companies or foundations alone
- 6Fictitious operating systems
- 7Notes and references
- 8Related Articles
- The main [ edit | change the code ]
- Microsoft Windows (latest version: Windows 10): Microsoft’s operating systems are currently preinstalled on more than 91% of personal computers [ref. necessary] .
- Derivatives of Unix (in different versions: BSD, System V, etc.) of which:
- macOS and iOS (ex-iPhone OS): pre-installed systems on the majority of computers and mobile devices sold by Apple (formerly MacOS X and;
- GNU / Linux : a free operating system based on the Linux kernel and GNU tools installed on + 1% of the global computer park all distributions combined [ref. necessary] .
- GNU / Linux fathers systems: Arch Linux , Debian , Gentoo , Red Hat , SUSE , Slackware , …
- GNU / Linux child systems: see the list of Linux distributions
- the BSD family : a successful effort to make the Berkeley system free, including:
- NetBSD , OpenBSD and its derivative OliveBSD, FreeBSD and its derivatives PicoBSD , DragonFly BSD and PC-BSD ; Darwin (which is built on Mac OS X, semi-owner), OpenSolaris from Sun .
- the so-called ” proprietary ” Unix :
- AIX ( IBM , SystemV), A / UX ( Apple , SystemV), BOS ( Bull Operating System), IRIX ( Silicon Graphics , SystemV), HP-UX ( Hewlett-Packard , SystemV), LynxOS ( LynuxWorks ), NeXTSTEP ( NeXT , BSD), Sinix (Siemens), Solaris ( Sun , SystemV), SunOS ( Sun , BSD), Tru64 ( Compaq ).
- OS / 2 from IBM and its successor eComStation 1 ;
- OS / 400 present on IBM system resources (AS / 400 – ISeries);
- VMS and OpenVMS (Supported by HP who bought Compaq , formerly Digital );
- mainframe operating systems (“large systems”):
- Multics (father of UNIX) and heir to CTSS
- IBM: MVS , VM , DOS / VSE , TPF
- Bull: GCOS
- Siemens: BS2000
- ITS, TOPS-10 and TOPS-20
- PipinOS; Bass under BeOS developed in C by UmiXTY Computer Software Inc.
- Other operating systems [ edit | change the code ]
- AcidOS, a French operating system written in C and assembler , intended to secure and make reliable the industrial computer systems of the server to IoT;
- Android , open source operating system with Linux kernel for tablets and smartphones , and Android x86 for computer;
- AmigaOS , the operating system of the Amiga ;
- AROS , free operating system AmigaOS-like;
- AtheOS , which is no longer maintained;
- Bada , operating system for PDAs ;
- BeOS , Be , the company that produced it was bought by Palm which itself was bought by HP, the system is no longer maintained. see HaikuOS ;
- Cherry OS , a new operating system based on the openSUSE kernel of Gamecom’s InCorp micro enterprise. currently [when?] developing;
- ChorusOS ;
- Coherent ;
- Contiki , very small system, suitable for embedded applications and working on many targets;
- Cosmos ;
- CP / M , written in PL / M by Gary Kildall and ancestor of DOS ;
- Chromium OS , open source version of Google Chrome OS ;
- eCos , written by Cygnus then RedHat , today a free software ;
- elementary OS ;
- EmuTOS , a free system whose purpose is to replace the TOS to be able to use the Atari ST emulators legally;
- EPOC , 32-bit Preemptive Multitasking for Psion Series 5;
- E / OS LX , Windows and Linux compatible;
- FreeDOS , DOS compatible with MS-DOS and PC-DOS open source and free;
- GNU / Hurd , the operating system GNU based microkernel Mach ;
- Google Chrome OS , browser-based system Google Chrome with a Linux kernel;
- GS / OS , the operating system of the Apple II GS ;
- HaikuOS , project to completely rewrite BeOS under a free license.
- Illumos , a fork of OpenSolaris to remove all parts of OpenSolaris whose code is not considered free and whose stated purpose is to keep an ABI 100% compatible with OS / NET Solaris / OpenSolaris .
- iRMX , a real-time multitasking operating system by Intel ;
- Isaac, an operating system written in Lisaac ;
- Jolicloud , a simplified Linux-based operating system for cloud-based Web use;
- KerpleOS, Windows NT Family Exploitation System written in C ++, compatible with Windows and ReactOS (Developer by Umixty Computer)
- Lepton 2 , a POSIX open source operating system supported by O10ée 3 and dedicated to real-time embedded systems;
- Linutop , a simplified Linux-based operating system for use in the internet, digital signage and monitoring;
- Logram, a Linux-based operating system;
- LynxOS , Unix real-time operating system for embedded systems and critical software ;
- Maemo , embedded operating system in tablets from Nokia ;
- MagiC , multitasking system for Atari ST . Also available as emulators for PC (MagiCPC) and Macintosh (MagiCMac);
- MeeGo , merger of Maemo ( Nokia ) and Moblin ( Intel ) for mobile devices.
- MorphOS , community attempt to produce an AmigaOS-like system;
- Minix , a Unix clone based on a micro-kernel created by Andrew S. Tanenbaum for educational purposes;
- MiNT , a multitasking kernel inspired by BSD Unix systems for TOS- enabled computers . Compatibility with old applications is preserved (to a certain extent);
- NetWare , server-only operating system, edited by Novell. First platform hosting the Novell eDirectory Metadirectory (as NDS at the time, for Novell Directory Services). Novell ceased support in March 2010, prompting to migrate to Novell Open Enterprise Server based on SUSE Linux Enterprise Server;